Crowns in Pediatric Dentistry
 High incidence of dental cavities among children is one of the leading causes for pediatric dental crowns.
High incidence of dental cavities among children is one of the leading causes for pediatric dental crowns.
Crowns in Pediatric Dentistry
Pediatric crowns are tooth shaped covers that are given for primary or young permanent teeth which are decayed, fractured and non-restorable.
The varieties of crown are:
• Stainless Steel
• Strip Crowns
• Polycarbonate Crowns
• Bioflex Crowns
• Zirconia Crowns
High incidence of dental cavities among children is one of the leading causes for pediatric dental crowns.
Common questions from parents regarding pediatric crowns:
- Why are crowns necessary over milk teeth which will shed later?
- Crowns are given in milk teeth to establish the natural width of the crown. Due to dental caries, if the crown size is diminished then the new erupting teeth will not have enough space causing more problems down the road.
- What is the procedure of pediatric crowns placement, how many visits are needed?
- The crowns for primary teeth are done in a single setting, since they are available in pre-fabricated sizes, from 2-7. The tooth is trimmed and the crown is placed immediately based on their sizing.
- Do we have to remove the caps later in the future?
- The pediatric crowns shed on their own along with milk tooth as the permanent tooth sprouts from beneath the milk tooth
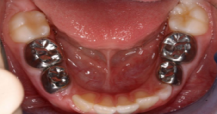
Stainless Steel Crowns:
These are pre-formed crowns composed of 67% iron, 10%-13% nickel, 17%-19% chromium and 4% of other minor metals. These crowns are pre-trimmed, contoured and available from sizes 2-7 which are fixed immediately after prepping with cement.


Polycarbonate crowns:
They are thermoplastic crowns. These are available in pre-formed sizes. They are comparatively weaker and cannot withstand biting forces and are easily dislodged. These crows are also not esthetically appealing.


Strip Crowns:
Strip crowns are transparent plastic forms used for upper anterior teeth which are filled up with composite cement (tooth-coloured material). The drawbacks are, if not maintained properly dry restorative areas, can undergo colour change. The strength and functions of these crowns are better than polycarbonate crowns but esthetically they’re still not upto the mark.


Zirconia Crowns:
These crowns are monolithic stabilized tetragonal polycrystal which are very stable, strong with very good esthetic properties. These crowns are slightly more expensive when compared to the other crowns. Good work comes as good rate. These are also pre-formed and available in different sizes and can be fixed on the same visit.


Bioflex Crowns:
These crowns are flexible, durable, self-adaptable and esthetic pre-formed crowns. These have properties of both stainless steel and zirconia.

Conclusion:
Pediatric crown placements are usually painless but they are essential part in saving the milk teeth from cavities to prevent it from shedding earlier than anticipated and to protect the strength of the teeth after root canal treatment, or to protect young permanent teeth from cavities early on in their lives.